

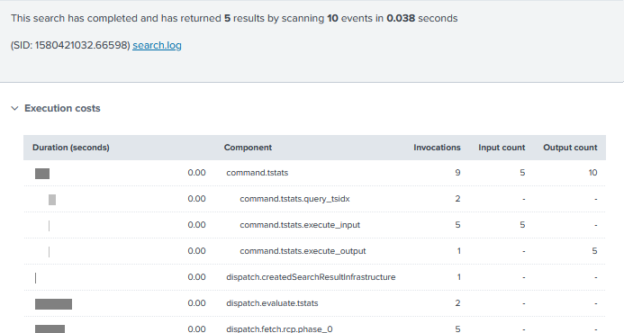
To determine what that field should be set to, perform a conditional check to see if the latest event time is greater (more recent) than the current time minus 5 minutes. The earliest event should go to a maximum of 24 hours in the past and group this data by the host name.Ĭreate a new field called “recent”. Run a tstats search to pull the latest event’s “_time” field matching on any index that is accessible by the user. Let’s take a look at the SPL and break down each component to annotate what is happening as part of the search: Screenshot of Splunk showing host without any new events in last 5 minutes. | eval recent = if(latest > relative_time(now(),"-5m"),1,0), realLatest = strftime(latest,"%c")įigure 1. | tstats latest(_time) as latest where index=* earliest=-24h by host In the case where you want to be notified when events are no longer being received by a certain host, a search can be crafted to compare the timestamp of the events from the host to the relative time window. Alert When There is No Data From a Specific Host Once we understand these items, we can now craft a search within Splunk to detect and alert when an event has not been received.
#SPLUNK TSTATS HOW TO#
conf16 presentation entitled " How to Scale: From _raw to tstats (and beyond!)." Special Considerations Side note: for a quality explanation of tstats (and just accelerating access to data in Splunk), reference this amazing. In fact, my initial iteration was totally different (and totally inefficient) and after discussing with some colleagues, they helped me accomplish the same outcome with a much faster search. There’s an article that talks about how to monitor inactive hosts using metadata.
Let me preface this section of the article by saying that with Splunk, there is definitely more than one way to accomplish this.
Doing this will allow you to not only understand “what” works, but the “how” and “why” behind it. A Bit of Backgroundīefore getting right into the meat and potatoes of how to accomplish this, let’s take a short detour to try to explain the methodology behind the upcoming SPL. In this blog, I aim to share with you some ideas on how to answer this with Splunk using Search Processing Language (SPL). Surprisingly, with this being such an often-asked question, I haven't been able to find much documentation on how to accomplish this using the native features of Splunk. As a matter of fact, if I had $0.05 each time I was asked this question, I would have $0.25! So I've only been at Splunk for 8 months, and in the short amount of time I've been here, one of the most common questions I've been asked is “How do I get an alert when Splunk is not receiving logs?".


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
